
And as conscious beings we like to find patterns, and we find equivalencies interesting, especially when the things being equated are "important" or "epic" (like neurons and stars). That's why journalists report distances as number of football fields, mass as number of fully-loaded 747s, energy in terms of Hiroshima bombs, etc.Even though we can't conceive of the number of stars in the Milky Way or the number of neurons in the human brain, equating the two gives people a sense of enormity.
"This is a phrase a lot of science communicators like to use because giving people a sense of scale when it comes to large numbers is so difficult. " Are There Really as Many Neurons in the Human Brain as Stars in the Milky Way? " from Scitable by Nature Education. Want to learn more? Check out this article and paper: Pramod RT, Postdoctoral Associate, MIT Dept. Learning Data Representation: Hierarchies and Invariance. 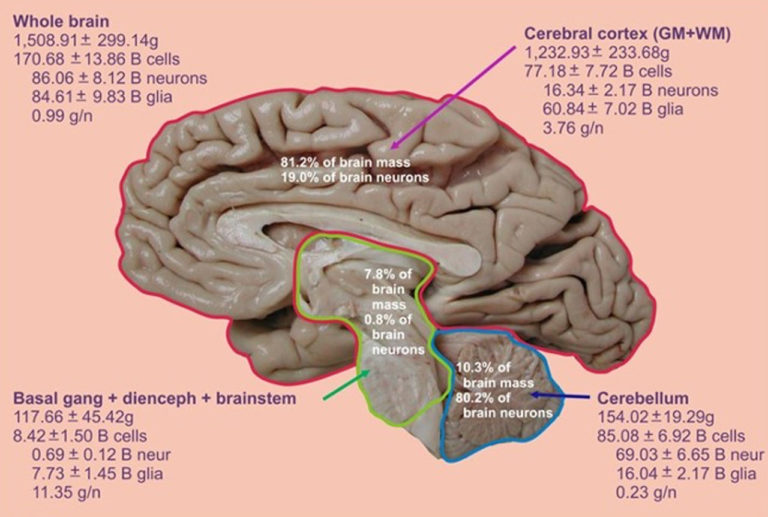 Engineering and Reverse Engineering Reinforcement Learning. Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) 2015. Biophysical principles of brain oscillations and their meaning for information processing. Deep Learning: Theory, Algorithms and Applications. CBMM Workshop on Speech Representation, Perception and Recognition. Science of Intelligence: Computational Principles of Natural and Artificial Intelligence. A workshop on language and vision at CVPR 2017.
Engineering and Reverse Engineering Reinforcement Learning. Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) 2015. Biophysical principles of brain oscillations and their meaning for information processing. Deep Learning: Theory, Algorithms and Applications. CBMM Workshop on Speech Representation, Perception and Recognition. Science of Intelligence: Computational Principles of Natural and Artificial Intelligence. A workshop on language and vision at CVPR 2017. 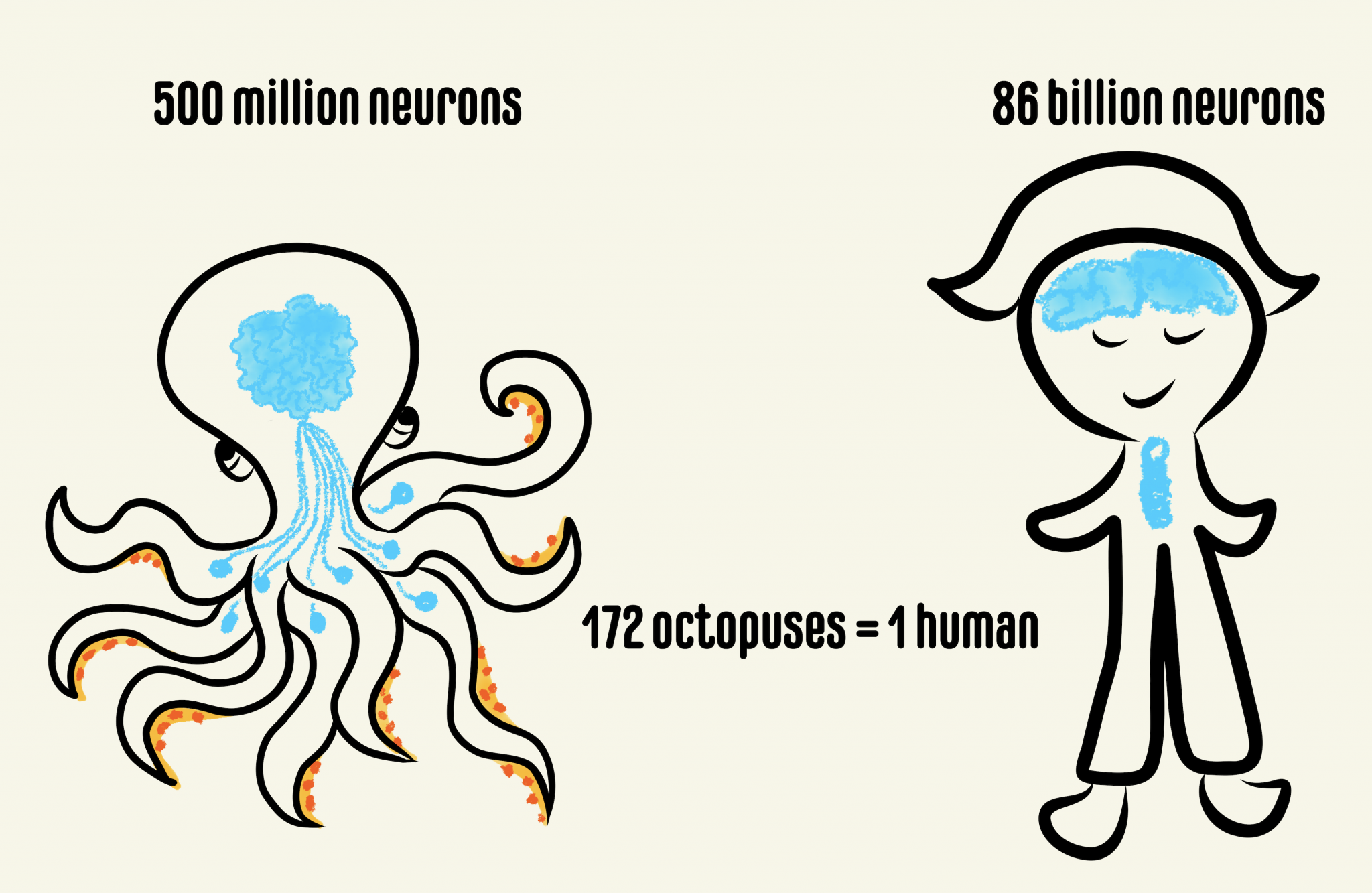
Learning Disentangled Representations: from Perception to Control.A workshop on language and vision at CVPR 2018.A workshop on language and vision at CVPR 2019.Shared Visual Representations in Human and Machine Intelligence (SVRHM) Workshop 2019.MLCC 2020 simula Machine Learning Crash Course.REGML 2020 | Regularization Methods for Machine Learning.Shared Visual Representations in Human & Machine Intelligence (SVRHM) 2020.Shared Visual Representations in Human & Machine Intelligence (SVRHM) 2021.Shared Visual Representations in Human & Machine Intelligence (SVRHM) 2022.

Information-Theoretic Principles in Cognitive Systems. Undergraduate Summer Research Internships in Neuroscience. Theoretical Frameworks for Intelligence. Neurally-plausible mental-state recognition from observable actions. Sleep Network Dynamics Underlying Flexible Memory Consolidation and Learning. Invariance in Visual Cortex Neurons as Defined Through Deep Generative Networks. Computational models of human social interaction perception. Modeling Human Goal Inference as Inverse Planning in Real Scenes. Memory and Executive Function | Brain OS.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
